Creating Unique Logos: The Role of Boolean Operations in Modern Design
What are Boolean Operations?
Named after the mathematician George Boole, Boolean operations represent a branch of algebra that involves values of true and false, generally referred to as binary values. In the context of graphic design, Boolean operations are used to manipulate graphic objects, mainly through set operations like Union, Intersection, Difference, and Exclusion. These operations allow designers to combine or partition shapes in simple and intuitive ways to create complex graphics and icons.
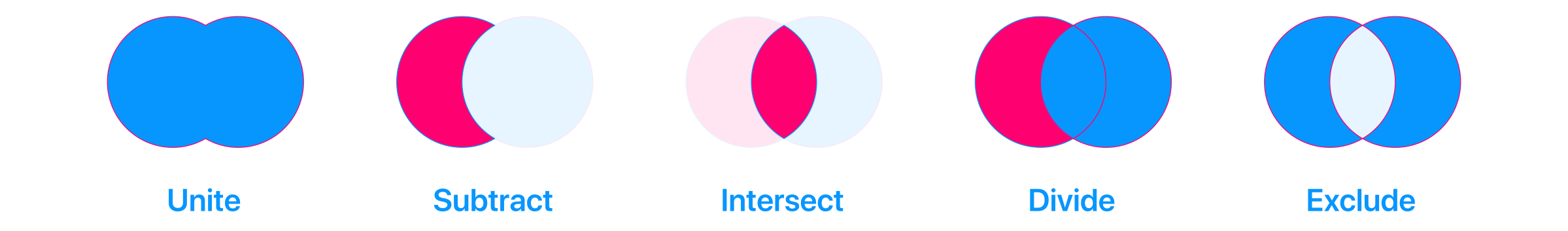
Union: Combines two objects together, also known as addition
Subtract: Uses the Boolean object to cut away from target objects, also known as subtraction
Intersect: Combines shape layers
Exclude: Combines shape layers
Divide: Turns two objects into three
Practical Examples of Boolean Operations in Use
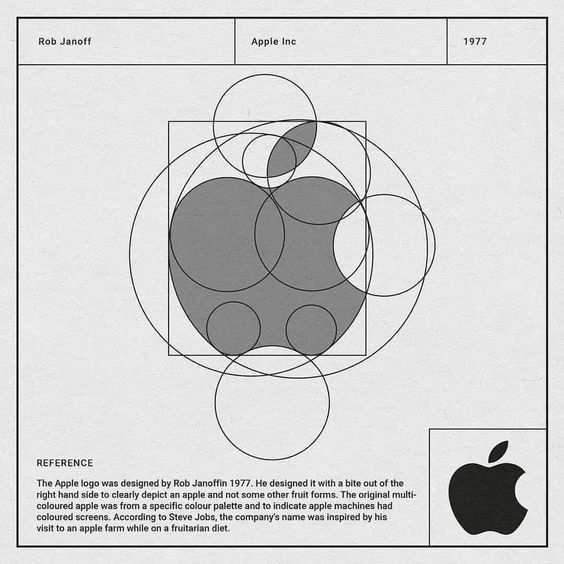
Apple
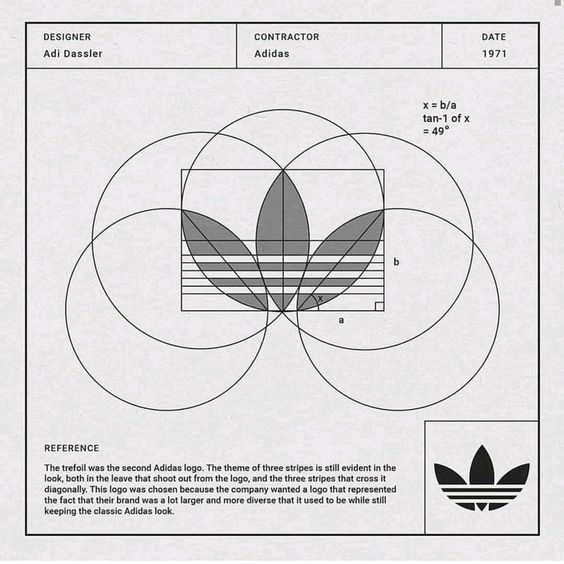
Adidas
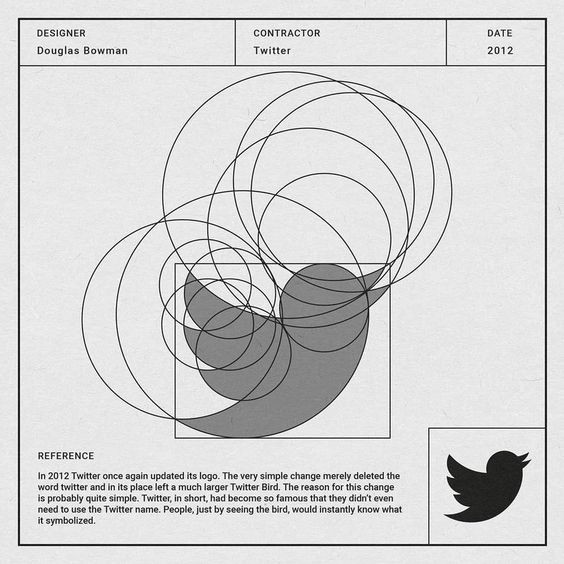
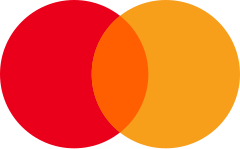
Mastercard
Audi

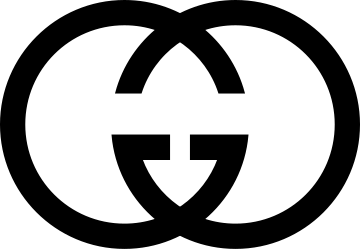
Gucci
How to Use Boolean Operations in Figma
After selecting a group of shape layers in Figma, click on the "More Options" in the "Exclude" section in the right-hand menu to access the Boolean operations feature options.
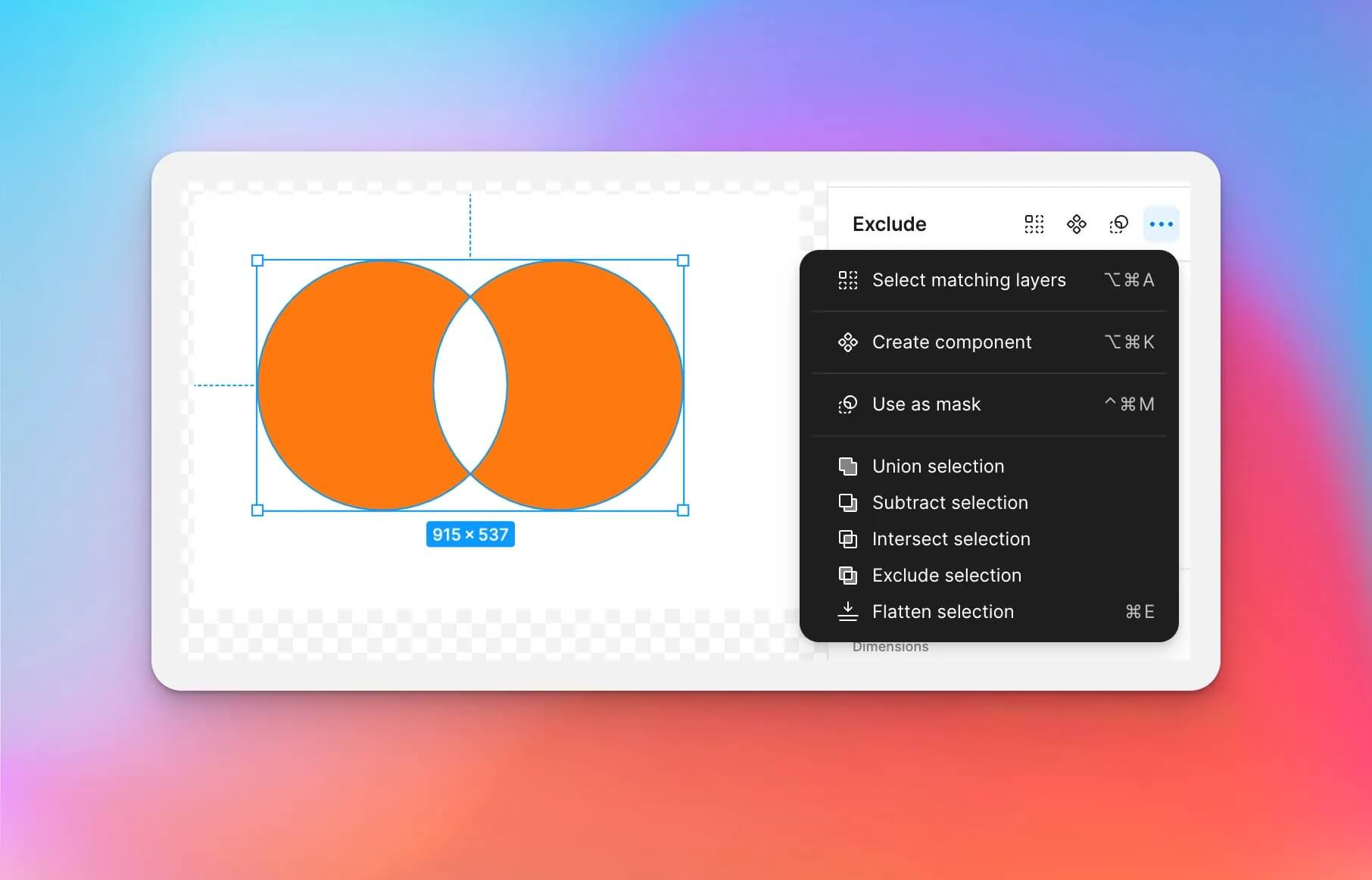
Boolean groups are treated as a single shape layer and share fill and stroke properties and can be combined with other boolean groups through subsequent boolean operations.
- Union selection: Union combines the selected shapes into a boolean group. If the objects overlap, the new shape’s outer path consists of the composite of its sublayers’ paths minus any segments that overlap. The stroke would then be applied to that outer path ignoring any path segments which overlap each other.
- Subtract selection: Subtract is the opposite of union. Subtract removes the area of a shape or set of shapes from a base shape. Only the bottom shape layer is solid, the rest are subtracted from it.
- Intersect selection: Intersect creates a boolean group whose shape consists only of the overlapping parts of its sublayers.
- Exclude selection: Exclude is the opposite of intersect. Exclude shows only the areas of its sublayers that do not overlap.
- Flatten selection: Creates a single layer from the selected shapes.